How to Choose the Best Semiconductor Test Socket for Your Needs?
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, the choice of a semiconductor test socket is crucial. As industry expert Dr. Emily Chen states, “Selecting the right semiconductor test socket can elevate your testing accuracy.” This emphasizes the importance of making an informed decision.
A semiconductor test socket plays a vital role in the testing process. It ensures proper connections between the semiconductor device and testing equipment. However, the variety of options can be overwhelming. Common mistakes include choosing a socket based on price rather than performance. Features such as thermal management and pin count are often overlooked.
Consider how different applications may require distinct socket specifications. For instance, high-frequency devices need sockets that minimize signal loss. Reflecting on past choices can lead to improved decisions in the future. Evaluating your specific testing requirements will guide you toward the best semiconductor test socket for your needs.
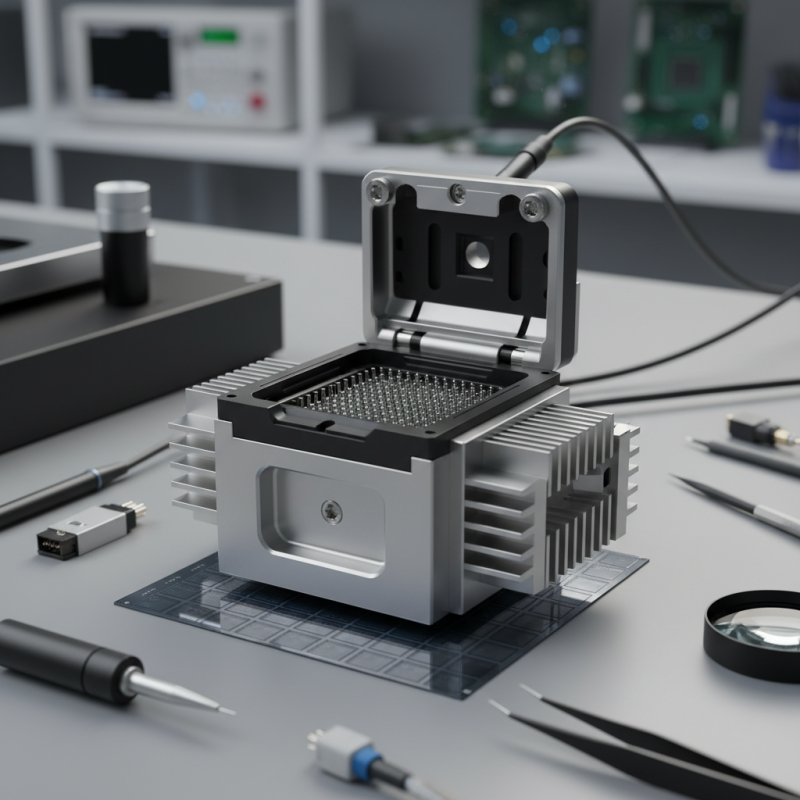

Understanding the Basics of Semiconductor Test Sockets
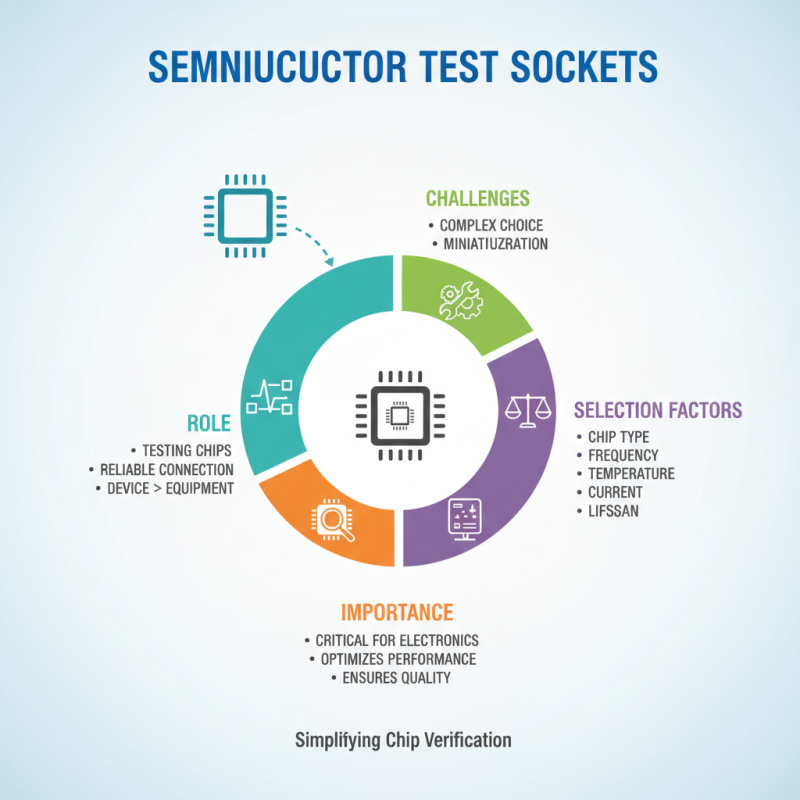
Understanding semiconductor test sockets is essential for anyone working in electronics. These sockets serve a vital role in testing chips. They provide a reliable connection between the semiconductor device and measurement equipment. Choosing the right test socket can be complicated. Various factors influence the decision.
A good test socket should fit the specific chip package. Misalignment can lead to inaccurate results. Proper contact is crucial for signal integrity. Thermal performance is equally important. Some designs might not manage heat well, affecting the testing process. Think about your testing environment. High-frequency applications have unique requirements.
While selecting a socket, consider the number of contacts. Too few can limit functionality. However, too many may lead to complexity. Also, be prepared for some trial and error. It's natural to make mistakes when selecting your socket. Learn from each experience instead of seeking perfection. Every decision contributes to improving your testing setup.
Identifying Your Testing Requirements and Specifications
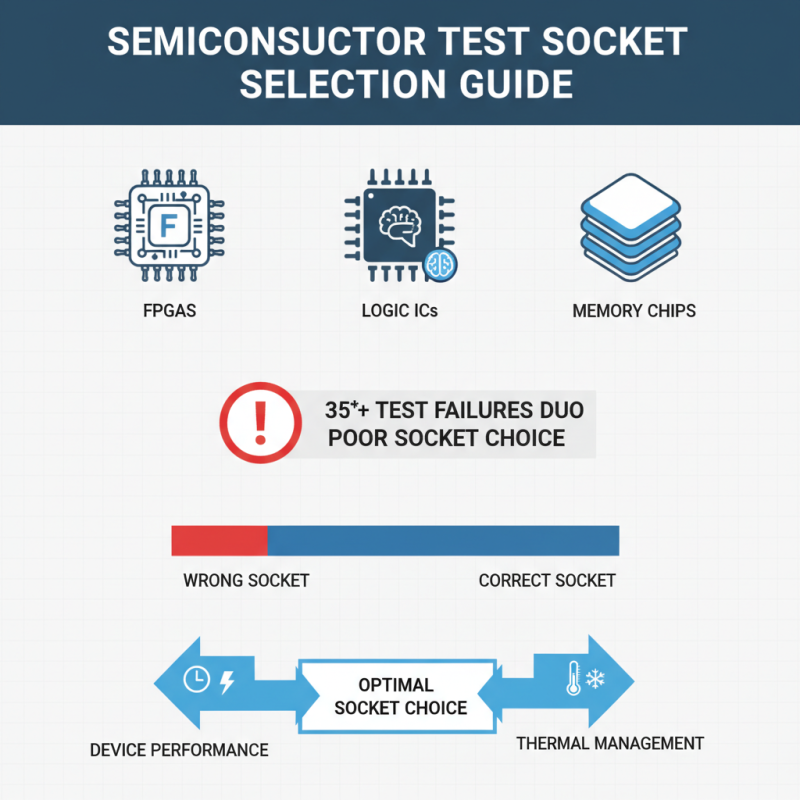
Choosing the right semiconductor test socket requires a clear understanding of your specific testing requirements. Begin by evaluating the type of semiconductor devices you are testing. For instance, different devices such as FPGAs, logic ICs, or memory chips may require distinct socket configurations. According to industry reports, over 35% of test failures are linked to poor socket choices. Thus, it’s crucial to align your socket selection with your device’s performance characteristics and thermal management needs.
Next, consider the operating frequency and signal integrity requirements. High-speed applications demand sockets that can handle greater bandwidths without introducing excessive parasitics. Many manufacturers suggest that sockets supporting frequencies above 10GHz are often necessary for modern applications. In contrast, some designs may not need such high specs, which might increase costs unnecessarily. Think critically about whether your needs align with these parameters or if adjustments are needed.
Finally, look into your budget and production volume. A high-quality socket can be a significant investment, impacting your project’s overall cost. Reports indicate that high-performance sockets may increase expenses by 20-30%. However, cheaper alternatives may lead to increased failure rates, which could cost more in the long run. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision.
Evaluating Different Socket Types and Their Applications
When selecting a semiconductor test socket, understanding the different types is crucial. The most common types include
spring-loaded pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets, and non-ZIF sockets. Each type has unique features and applications.
Spring-loaded pins are known for their reliability and longevity, while ZIF sockets allow easy insertion and removal of devices. Non-ZIF sockets tend to provide better contact at lower costs, making them suitable for high-volume production.
According to industry reports, the semiconductor test socket market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% through 2028. Choosing the right socket type can impact not just testing efficiency but also overall manufacturing costs. Specific applications require different socket designs. For instance, high-speed digital testing often benefits from ZIF sockets due to their ability to reduce physical stress on the device.
Tip: Evaluate your expected testing volume. Low-volume tests might work best with ZIF sockets, while a high-volume environment may favor non-ZIF options for cost-effectiveness.
It's essential to address potential shortcomings, too. Each socket type may not fit all scenarios. For example, spring-loaded pins, while durable, can sometimes lead to inconsistent contact if not maintained properly. Assess the drawbacks of each type in your unique context.
Tip: Keep a maintenance log. Regular checks can prevent performance issues and extend socket life.
Considering Material and Environmental Factors in Socket Selection
Choosing the right semiconductor test socket can be complex. Material and environmental factors play crucial roles in this process. The socket material affects durability and performance. Consider the temperature range it will face. High temperatures may cause degradation. Some materials do not perform well under harsh conditions.
When thinking about your specific requirements, evaluate whether the socket is exposed to moisture, dust, or chemicals. These elements can impact the performance and lifespan of your sockets. Selecting a socket made from resistant materials can help. However, some materials may offer less flexibility or require special handling.
Tips: Always check the compatibility of the socket with your devices. Test sockets made from different materials to see which one offers optimal performance. Do not overlook the environment. Sometimes, a cheap socket may seem convenient, but it might not endure the conditions. Experimentation might be necessary, and finding the perfect match could take time.
Assessing Cost and Availability of Semiconductor Test Sockets
When selecting semiconductor test sockets, cost and availability are crucial factors. The market shows a steady increase in demand. A recent report by Market Research Future indicated that the semiconductor test socket market could grow at a CAGR of 6.5% between 2021 and 2028. Companies must choose wisely to optimize spending. Some sockets might seem affordable upfront but require costly accessories or frequent replacements.
Additionally, consider sourcing challenges. Supply chain disruptions have led to increased lead times. A recent study highlighted that over 30% of electronic manufacturers reported longer wait times for essential components, including test sockets. This situation underscores the importance of assessing availability. Businesses might rely on local suppliers for quicker access, even if costs are slightly higher. Evaluating potential delays is essential to maintain project timelines.
Balancing cost and availability is a difficult task. While low prices attract attention, they can hide potential issues. It's essential to assess long-term performance and compatibility. An effective socket will minimize testing errors and enhance productivity. Ignoring these aspects could lead to unforeseen expenses down the line.
How to Choose the Best Semiconductor Test Socket for Your Needs? - Assessing Cost and Availability of Semiconductor Test Sockets
| Socket Type | Cost (USD) | Availability | Temperature Range (°C) | Contact Resistance (mΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin Grid Array (PGA) | 150 | In Stock | -40 to 125 | 5 |
| Ball Grid Array (BGA) | 200 | Pre-order | -40 to 150 | 8 |
| Chip-on-Board (COB) | 120 | In Stock | -30 to 125 | 10 |
| Custom Test Socket | 250 | Made to Order | -40 to 125 | 7 |
| Land Grid Array (LGA) | 180 | In Stock | -40 to 125 | 6 |
Related Posts
-

Top Trends in Semiconductor Test Sockets for 2025 You Need to Know
-

The Ultimate Guide to Selecting the Right Semiconductor Test Socket for Your Needs
-

Unlocking the Secrets of IV Curve Tracers for Enhanced Electronic Testing
-

How to Choose the Right Pogo Pins for Your PCB Design Needs
-

Innovative PCBA Testing Solutions Transforming Global Supply Chains
-

2025 Top 10 Test PCB Innovations Transforming Circuit Board Development
