10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Semiconductor Test Socket
Choosing the right semiconductor test socket is crucial for efficient testing and reliability. These components play a pivotal role in ensuring quality and performance. With numerous options available, it can be overwhelming to make the best choice.
When selecting a semiconductor test socket, consider factors such as compatibility and thermal performance. Each socket must fit various semiconductor devices perfectly. The right material can enhance signal integrity, influencing test outcomes significantly. Testing protocols and environments also impact the choice.
It’s easy to overlook specific details in the selection process. Mistakes can lead to increased testing time or even device damage. Take time to review specifications thoroughly. Failing to do so can result in costly errors. A thoughtful approach can lead to more accurate results and better performance in the long run.

Understanding the Role of Semiconductor Test Sockets in Device Testing
Semiconductor test sockets play a vital role in the testing process of electronic devices. They ensure reliable connections between the semiconductor chips and test equipment. The performance of these sockets can significantly impact test accuracy and efficiency. Reports indicate that poor socket choices can lead to increased test time by up to 25%. Therefore, selecting the right socket is crucial for optimal testing outcomes.
When choosing a test socket, consider the thermal characteristics. Some sockets do not dissipate heat effectively, which can lead to erroneous test results. It’s essential to assess the socket’s thermal management features to prevent overheating. Additionally, ensure the socket is compatible with your specific device type. Incompatible sockets can result in physical damage or test failures.
Tip: Always evaluate the socket's material and design. High-quality materials can resist wear and maintain signal integrity. Another tip: conduct thorough tests in your specific conditions before finalizing your choice. This helps in identifying potential issues early on. Remember, a socket that works well in one setting may not perform the same in another. Striving for the perfect fit is an ongoing process.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Semiconductor Test Socket
| Tip | Description | Consideration | Impact on Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Compatibility | Ensure the socket is compatible with the device under test (DUT). | Check pin arrangements and contact types. | Avoids physical damage to DUT and ensures accurate testing. |
| 2. Thermal Management | Select sockets that provide adequate thermal dissipation. | Consider materials and design that enhance heat flow. | Maintains performance and prevents overheating. |
| 3. Contact Resistance | Assess the contact resistance of the socket. | Look for low resistance contacts to ensure signal integrity. | Improves measurement accuracy and reliability. |
| 4. Socket Lifespan | Choose a socket with a proven lifespan. | Evaluate the material durability and usage cycles. | Reduces replacement costs and downtime. |
| 5. Ease of Use | Consider user-friendly designs for quick setup. | Look for features that simplify handling during testing. | Speeds up test cycles and enhances efficiency. |
| 6. Testing Environment | Choose sockets that suit the operational environment. | Consider factors like humidity, temperature, and vibration. | Ensures reliability under specific testing conditions. |
| 7. Cost Considerations | Find a balance between quality and cost. | Assess value versus budget constraints. | Maintains operational efficiency without overspending. |
| 8. Manufacturer Support | Consider manufacturers that offer good support and documentation. | Research customer service reputation. | Facilitates troubleshooting and maintenance. |
| 9. Versatility | Select sockets that can accommodate multiple devices. | Look for adjustable or multi-use designs. | Increases testing capabilities and flexibility. |
| 10. Technical Specifications | Review detailed technical specs to match requirements. | Pay attention to voltage, current, and frequency ratings. | Ensures correct performance in various testing scenarios. |
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a Test Socket for Semiconductors
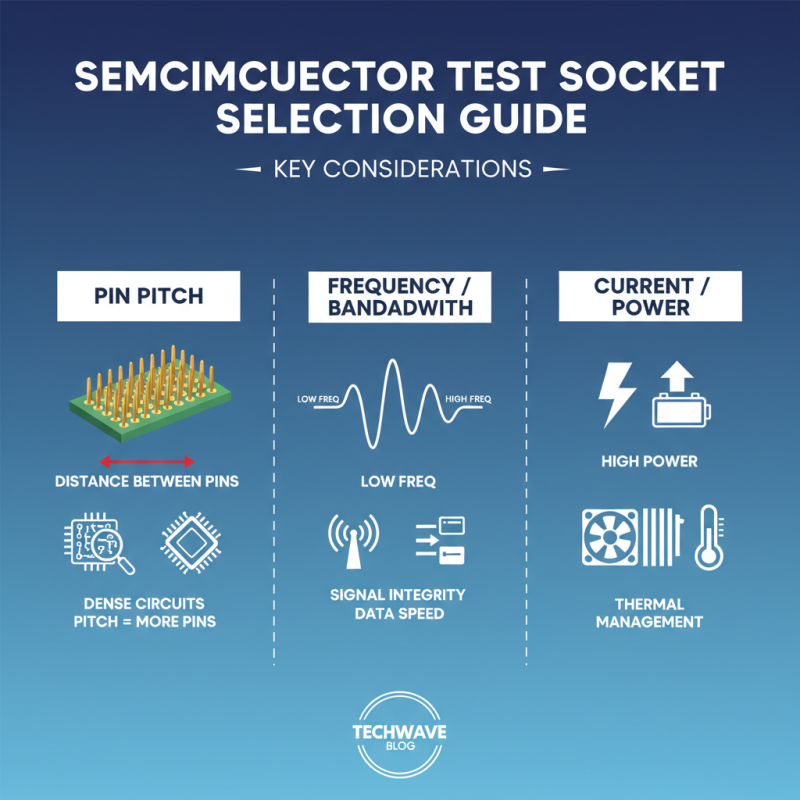
Choosing the right semiconductor test socket requires careful consideration of several key specifications. One major aspect is pin pitch. The distance between pins can affect your circuit’s performance. A smaller pitch can accommodate more pins, but it may be harder to manufacture reliably. If you're working with dense circuits, ensure the socket can handle the tight spacing.
Another critical factor is the socket material. It affects heat resistance and signal integrity. For high-frequency applications, materials with low dielectric constants are preferable. They maintain signal fidelity but might be more expensive. Test sockets should also be evaluated for durability. Frequent use can lead to wear and tear, so it’s essential to choose a robust design. Reflect on how many cycles you'll need. This can guide you in selecting a socket that meets your testing demands without unnecessary costs.
Lastly, consider the contact force. It plays a crucial role in ensuring a good electrical connection. Insufficient force can lead to intermittent faults. Working with too much force can damage components. Balancing these specifications is an ongoing challenge. Regularly reassess your needs as technology changes. Making informed choices can significantly impact your testing efficiency and the overall success of semiconductor development.
Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness: Testing Socket Prices vs. Performance Metrics
Choosing the right semiconductor test socket demands careful evaluation of cost-effectiveness. Prices vary widely, but they don't always correlate with performance. A study by the Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI) indicates that lower-priced sockets can lead to testing inefficiencies. Over time, these inefficiencies may result in increased production costs.
Performance metrics are crucial. High-quality sockets often deliver better thermal management. This can enhance testing accuracy and reduce cycle times. According to a recent report, companies that invest in superior sockets see a 25% increase in throughput. However, the initial investment can be daunting. Many engineers struggle to justify these expenses when budgets are tight.
Performance decline is another consideration. A less expensive socket may degrade faster. This can lead to higher replacement costs and potential downtime. Some users report that cheaper options often compromise signal integrity. Regular assessments of performance against cost are vital. It’s important to reflect on whether short-term savings outweigh long-term implications. Balancing these factors can ultimately shape the testing strategy.
Cost-Effectiveness of Semiconductor Test Sockets
This chart compares the prices and performance metrics of various semiconductor test sockets. The data illustrates the relationship between cost and performance, helping manufacturers make informed decisions when selecting the right test socket.
Industry Trends: Latest Developments in Semiconductor Test Socket Technology
As semiconductor technology evolves, test sockets are becoming more sophisticated. Recent advancements focus on enhancing performance and reliability. This shift addresses the growing demand for miniaturized and high-speed devices. Engineers now prioritize precision and efficiency in choosing test sockets.
When selecting a semiconductor test socket, consider the pitch carefully. Smaller pitches can improve accuracy but may lead to more complex design issues. Also, think about the thermal management capabilities of the socket. Proper heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining performance.
Pay attention to the materials used in the socket. They must withstand repeated use and high temperatures. Sometimes, manufacturers overlook material quality, leading to premature failure. Lastly, ensure compatibility with current and future technologies. Evaluate how the socket will integrate with existing test systems. Balancing these factors can be challenging and requires thoughtful consideration.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compatibility with Various Semiconductor Packages
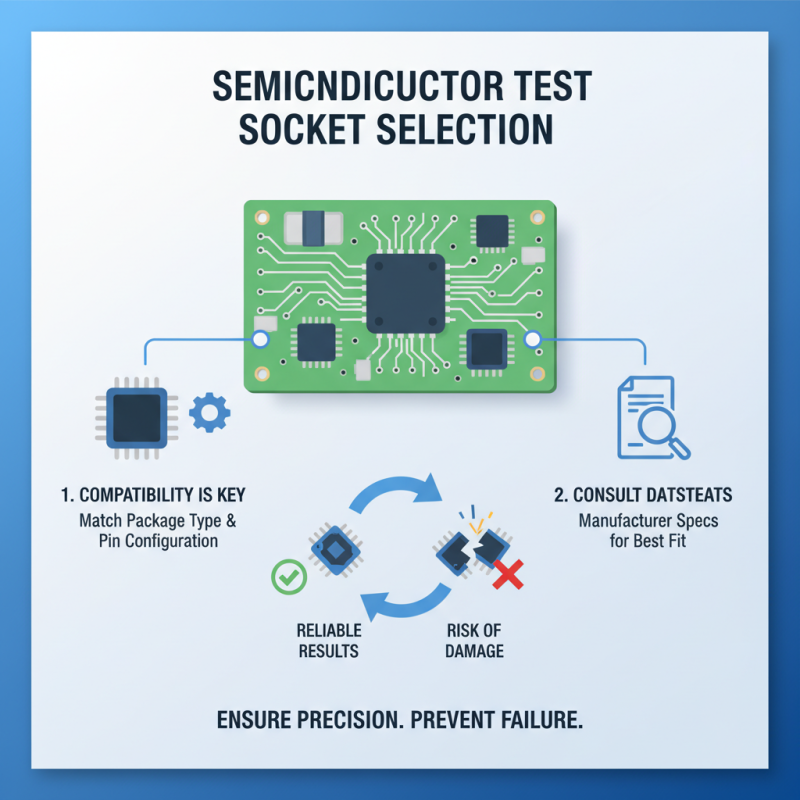
When selecting a semiconductor test socket, compatibility is crucial. Different semiconductor packages come with unique dimensions and pin configurations. Assessing these specifications is the foundation of a good choice. Mismatched sockets can lead to unreliable test results or even damage the components. It's advisable to refer to the manufacturer's datasheets. They offer valuable insights on what will work best.
Pay attention to the material of the socket. This aspect often gets overlooked. Materials like BeCu or phosphor bronze should be considered for their spring properties. Not all materials are created equal for heat resistance. Sometimes, trial and error may be necessary to find the perfect match. A socket that feels right may not perform well under stress or varying temperatures.
Don't forget about the testing environment. Some sockets work better in humid conditions, while others may corrode easily. Additionally, ensure that the socket supports the intended test frequency. This detail can greatly impact the accuracy of measurements. The right socket should ultimately align with both the application and environmental factors for effective testing.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Semiconductor Testing in Modern Technology
-

Top Trends in Semiconductor Test Sockets for 2025 You Need to Know
-

How to Use an IV Curve Tracer for Accurate Electrical Measurements
-

How to Choose the Right ICT Tester for Your Network Needs
-

Top 2025 Trends in PCBA Testing: Innovations and Techniques You Can't Miss
-

Tailored Solutions for Optimizing Your In Circuit Tester Performance
