10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Functional Testing Techniques
In the ever-evolving electronics industry, the importance of thorough testing cannot be overstated, particularly when it comes to PCB functional testing. This critical phase ensures that printed circuit boards operate as intended, filling a vital role in the overall reliability of electronic devices. As expert John Smith, a recognized authority in electronic manufacturing, aptly stated, "Effective PCB functional testing is the backbone of quality assurance in our industry." This sentiment underscores the necessity of implementing robust testing techniques to prevent failures that could lead to costly recalls or diminished consumer trust.
With the increasing complexity of modern electronics, manufacturers must adopt strategic approaches to PCB functional testing. From initial design validation to final production assessments, utilizing comprehensive testing methods is essential for identifying potential issues early in the process. This introduction will explore ten essential tips that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of PCB functional testing techniques, equipping engineers and testers with the knowledge to improve product quality and ensure a successful market launch. As we delve into these strategies, it becomes evident that meticulous attention to PCB functional testing can lead to substantial advancements in product integrity and customer satisfaction.
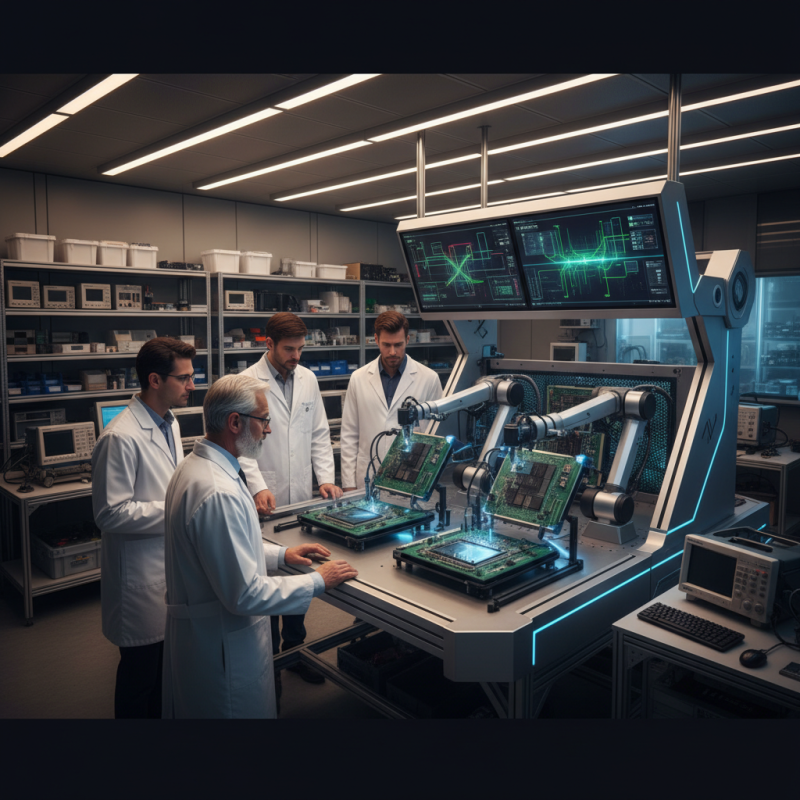

Understanding the Importance of PCB Functional Testing in Electronics
PCB functional testing is a critical process in the electronics manufacturing industry, ensuring that printed circuit boards operate as intended before they are deployed in consumer products. This testing phase serves multiple purposes, including verifying the functionality of each PCB, identifying defects early in the production cycle, and assessing overall performance. The importance of this testing cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in maintaining product quality and reliability, which ultimately leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and lower return rates.
In addition, PCB functional testing helps engineers and manufacturers meet stringent industry standards and regulations, which are essential for ensuring safety and compliance in electronic devices. By implementing robust testing techniques, companies can isolate failures more efficiently, allowing for timely corrective actions. This not only saves time and resources but also minimizes the risk of faulty products reaching the market. Thus, prioritizing effective PCB functional testing is not just about ensuring device performance; it’s about fostering a culture of quality and precision that is paramount in today’s competitive electronics landscape.
10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Functional Testing Techniques
This chart illustrates the importance level of various essential tips for successful PCB functional testing techniques. Each tip plays a crucial role in ensuring the functionality and reliability of electronic circuits.
Key Functional Testing Techniques: An Overview for Engineers
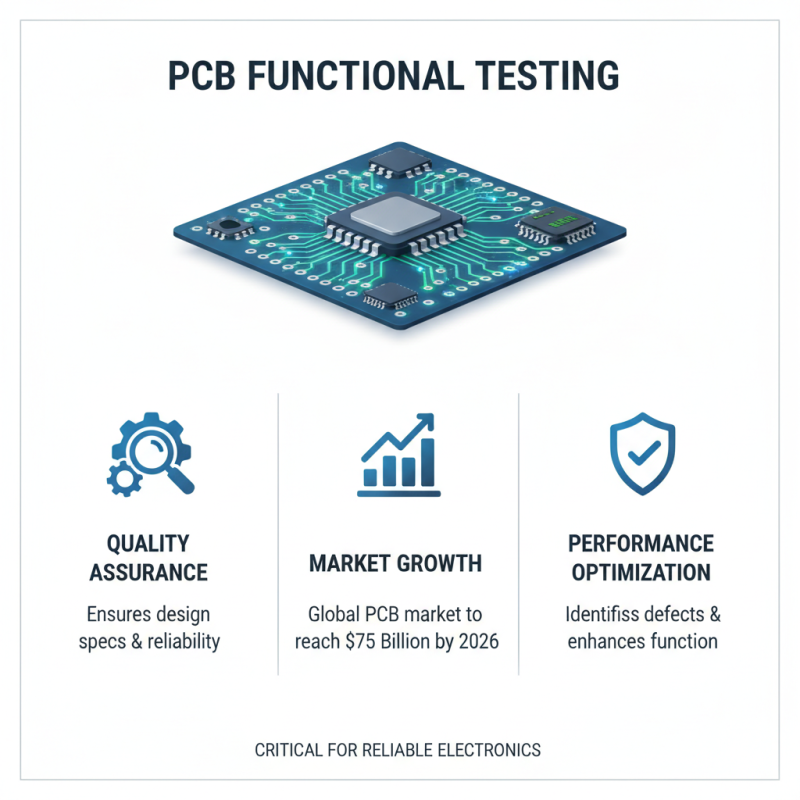
Functional testing is a critical phase in the lifecycle of printed circuit boards (PCBs), ensuring they meet design specifications and perform reliably. According to a report by IPC, the global PCB market is expected to reach USD 75 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing demand for effective testing techniques. Engineers must adopt comprehensive strategies to maintain high standards in functional testing, which serve not only to identify defects but also to optimize performance.
One essential tip for engineers is the implementation of automated testing systems. By leveraging software-driven approaches, engineers can increase test coverage and speed, substantially reducing human error. Research indicates that automated testing can lower test cycle time by up to 50%, greatly enhancing productivity. Additionally, engineers should prioritize thermal imaging during testing. This technique allows for the identification of thermal anomalies that could signal underlying issues, ensuring that temperature-related failures are addressed before they escalate.
Furthermore, engineers should consider incorporating a modular testing approach. This technique involves breaking down the PCB into smaller, manageable sections for testing, allowing for targeted evaluations of individual components. By doing so, defects can be isolated more efficiently, resulting in quicker resolutions and lower costs. Industry data shows that modular testing can lead to a decrease in overall debugging time by approximately 30%, underscoring its effectiveness in functional PCB testing.
Industry Standards and Compliance in PCB Functional Testing Processes
In the realm of PCB functional testing, adhering to industry standards and compliance regulations is paramount. Various international standards such as IPC-A-600, IPC-A-610, and ISO 9001 provide frameworks that guide manufacturers in ensuring product reliability and functionality. These standards define the acceptable quality levels for components, assembly processes, and overall performance. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can systematically evaluate their processes, reducing the likelihood of defects and enhancing end-product quality.
Compliance extends beyond mere adherence to standards; it involves rigorous testing protocols that assess a PCB's ability to perform under different conditions. Implementing standardized testing procedures ensures that each board meets specified performance criteria. Moreover, certification from recognized bodies can enhance a manufacturer's credibility in the market. This not only serves as an assurance to customers regarding product quality but also facilitates smoother interactions with regulatory bodies. Ultimately, prioritizing compliance with industry standards during PCB functional testing demonstrates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, fostering trust and long-term business success.
Critical Factors Affecting Reliability and Accuracy in PCB Testing
When conducting PCB functional testing, reliability and accuracy are the cornerstones of effective evaluation. One critical factor influencing these aspects is the test environment. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference can significantly impact the performance and results of testing. Maintaining a controlled environment minimizes external disturbances, ensuring that the test results reflect the true functionality of the PCB.
Another important consideration is the choice of testing methods and equipment. Selecting appropriate testing techniques such as in-circuit testing (ICT), functional testing, or automated optical inspection (AOI) can greatly improve the accuracy of results. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help in addressing specific reliability concerns. Additionally, the calibration of testing equipment and adherence to strict testing protocols are essential in achieving accurate measurements and reducing the risk of false negatives or positives in performance evaluations. By paying attention to these critical factors, engineers can enhance the reliability and accuracy of PCB functional testing processes significantly.
Utilizing Automated Testing Equipment for Enhanced PCB Testing Efficiency
In today's rapidly evolving electronics landscape, the efficiency of PCB functional testing plays a critical role in ensuring product reliability and performance. By leveraging automated testing equipment (ATE), manufacturers can significantly enhance their testing capabilities. Reports show that implementing ATE can reduce testing time by up to 70%, while also increasing accuracy and repeatability. This efficiency translates into faster time-to-market and reduced costs, critical factors for staying competitive in the industry.
One essential tip for successful PCB testing is to integrate automated test strategies early in the design phase. Early consideration allows for the development of test fixtures that can streamline the testing process. Additionally, utilizing software that automates data collection and analysis can aid in identifying defects more quickly, providing vital insights that can influence design adjustments. Another key aspect is the constant update of testing algorithms to accommodate new technologies—keeping pace with industry standards ensures that testing remains robust and relevant amid evolving technological demands.
Moreover, ensuring comprehensive training for personnel on ATE can maximize its effectiveness. A well-trained workforce not only operates equipment more proficiently but also understands how to interpret the data effectively, leading to improved diagnostics and quicker resolutions. As reports suggest, organizations that invest in staff training alongside technological upgrades see a marked improvement in overall testing outcomes, enhancing both the quality and speed of PCB assembly processes.
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize PCB Testing Methods for High Reliability and Reduced Costs
-

How to Choose the Right PCB Functional Testing Methods for Your Production Needs
-
2025 Top Insights on PCB Functional Testing for Electronics Reliability
-

Top 2025 Trends in PCBA Testing: Innovations and Techniques You Can't Miss
-
How to Effectively Conduct PCBA Testing for Quality Assurance
-

Essential Tips for Designing Custom Test Fixtures for Maximum Efficiency
