How to Use an IV Curve Tracer for Accurate Electrical Measurements
In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical engineering, precise measurements are paramount for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electronic components. The IV curve tracer has emerged as a crucial tool for engineers and technicians alike, enabling the analysis of current-voltage characteristics of various devices. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in semiconductor technology, emphasizes the significance of accurate measurements, stating, "An IV curve tracer is essential for understanding device performance, as it unveils the intricate relationship between current and voltage."
Utilizing an IV curve tracer can significantly enhance the accuracy of electrical measurements, providing insights that drive innovation in both research and practical applications. As professionals in the field seek to optimize designs and troubleshoot issues, mastering the use of this invaluable instrument becomes crucial. With its ability to produce detailed IV characteristics, the IV curve tracer not only aids in device characterization but also supports quality assurance in the manufacturing process. This introduction aims to guide users through the effective utilization of an IV curve tracer, highlighting its importance in achieving precise electrical measurements.

Understanding the Basics of IV Curve Tracers in Electrical Measurement
IV curve tracers are essential instruments for performing accurate electrical measurements, particularly in the characterization of semiconductor devices and solar cells. These devices provide a graphical representation of the current-voltage (I-V) relationship, allowing engineers to understand how a component behaves under varying electrical conditions. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), accurate I-V measurements can lead to significant improvements in device efficiency and performance, which is critical in industries like renewable energy and electronics.
The operation of IV curve tracers involves applying a range of voltages to a device and measuring the corresponding current. This test results in a curve that illustrates key performance metrics such as open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, and fill factor. Recent studies published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) indicate that using advanced IV curve tracing technology can enhance the accuracy of performance assessments by up to 15%, ensuring that devices meet or exceed regulatory and operational standards. This level of precision is particularly important as the industry moves towards stricter efficiency targets and more stringent quality control measures across both photovoltaic and electronic sectors.
By mastering the fundamentals of IV curve tracers and leveraging their capabilities, engineers can not only achieve detailed insights into device performance but also contribute to the ongoing improvement of technology and innovation in the electrical measurement landscape.
Key Components and Setup for Effective IV Curve Tracing
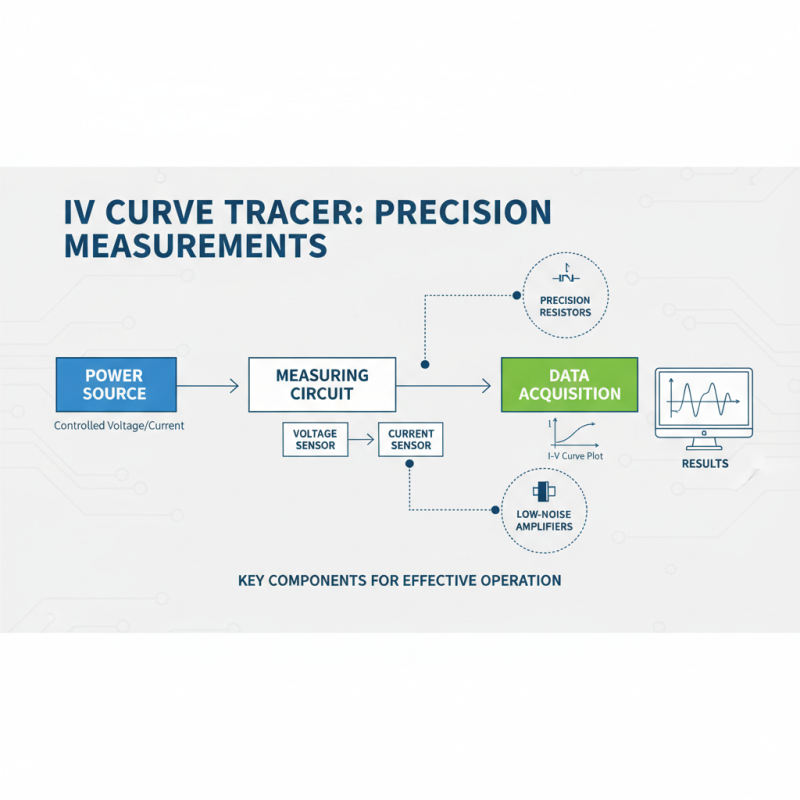
When utilizing an IV curve tracer for precise electrical measurements, understanding the key components and setup is essential for effective operation. An IV curve tracer typically consists of a power source, a measuring circuit, and data acquisition components. The power source provides a controlled voltage or current to the device under test (DUT), while the measuring circuit captures the resulting current and voltage values. According to industry reports, the accuracy of these measurements can be improved significantly with high-quality components, such as precision resistors and low-noise amplifiers, which reduce the impact of external noise and interference.
Proper setup is crucial for obtaining reliable IV curves. It is important to ensure that all connections are secure and that the DUT is functioning within its specified operating limits. The measuring software should be configured to collect data at appropriate intervals, typically within the range of milliseconds to seconds, depending on the dynamics of the tested device. Recent studies indicate that the most effective IV curve tracers can measure current in the picoampere range with resolutions exceeding 16 bits, facilitating the analysis of devices like solar cells or semiconductor junctions. By optimizing both hardware and software components, users can derive accurate insights and enhance the performance evaluations of their electrical devices.
Interpreting IV Curves: Analyzing Voltage and Current Characteristics
Interpreting IV curves is essential for understanding the voltage and current characteristics of electronic components and systems. An IV curve is a graphical representation that illustrates how current (I) varies with voltage (V) for a specific device under test. By analyzing these curves, engineers can derive critical parameters such as the open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, and fill factor, which collectively provide insights into the efficiency and performance of solar cells, diodes, and transistors. According to a study published by the International Journal of Electrical Engineering, accurate IV measurements can help improve the efficiency of photovoltaic systems by up to 15%, highlighting the importance of precise data interpretation.
To effectively interpret IV curves, one must consider not only the shape of the curve but also the surrounding environmental factors that may affect performance. For instance, temperature fluctuations can significantly influence the conductivity of semiconductor materials. Data indicates that a 10°C increase in temperature can lead to a reduction in the efficiency of silicon solar cells by 0.5% to 0.6%. Furthermore, the presence of resistive losses must also be evaluated, as higher series resistance can lead to a lower fill factor on the IV curve, indicating suboptimal performance. By leveraging accurate IV curve tracing and analysis, engineers can optimize device designs and improve overall system reliability and efficiency.
IV Curve Analysis of Solar Cells
This chart illustrates the IV (Current-Voltage) characteristics of a solar cell, showing the relationship between the generated current and the voltage output under standard test conditions.
Common Applications of IV Curve Tracers in Solar and Semiconductor Testing
IV curve tracers are essential tools in the fields of solar and semiconductor testing, providing critical insights into the performance and efficiency of various devices. In solar energy applications, these tools meticulously measure the current-voltage (IV) characteristics of photovoltaic cells. By plotting the IV curve, technicians can assess parameters such as open circuit voltage, short circuit current, and fill factor, which are crucial for determining the overall efficiency of solar panels. This data helps in optimizing the design and manufacturing process, ensuring that solar panels perform at their best under different environmental conditions.
In the semiconductor industry, IV curve tracers are used to evaluate the electrical properties of diodes, transistors, and other semiconductor devices. These measurements are vital for understanding device performance, including threshold voltage, saturation current, and breakdown voltage. By analyzing the IV curves, engineers can identify performance issues, characterize new materials, and refine the fabrication processes. This testing is crucial for developing reliable and efficient electronic components that meet the demands of modern technology, from consumer electronics to industrial applications.
How to Use an IV Curve Tracer for Accurate Electrical Measurements
| Application | IV Curve Tracer Features | Measurement Range | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Panel Testing | Real-time curve tracing, data logging | 0-1000V, 0-10A | Efficiency measurement, performance analysis |
| Semiconductor Testing | PIV (Peak Inverse Voltage) measurement | 0-1000V, 0-50mA | Characterizing diodes and transistors |
| Battery Testing | Temperature compensation, load testing | 0-60V, 0-100A | State of charge, discharge characteristics |
| Photovoltaic Module Evaluation | Automatic measurement, reporting | 0-1200V, 0-10A | Performance under different test conditions |
Best Practices for Accurate Measurements with IV Curve Tracers

To ensure accurate measurements with an IV curve tracer, it is crucial to follow certain best practices that optimize the performance and reliability of the device. First, before initiating any measurements, it is important to calibrate the tracer according to the manufacturer's specifications. This calibration process helps mitigate errors that may arise due to device drift or environmental factors. Additionally, using appropriate connection techniques, such as minimizing lead lengths and ensuring firm connections, can significantly enhance measurement accuracy by reducing potential noise and resistance losses.
Another key aspect of achieving reliable measurements is to conduct tests under controlled conditions. Performing measurements at a stable ambient temperature and avoiding fluctuations in humidity can prevent variations in the electrical properties of the device under test. It is also advisable to take multiple readings and average them to account for any anomalies or transient signals that may skew the data. Lastly, understanding the specific characteristics of the device being tested, including its voltage and current ranges, will aid in selecting the correct settings on the IV curve tracer, further refining the accuracy of the measurements. By adhering to these best practices, you can achieve more precise results with your IV curve tracer.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Secrets of IV Curve Tracers for Enhanced Electronic Testing
-

Exploring IV Curve Tracers: Innovative Applications and Industry Case Studies
-

Tailored Solutions for Optimizing Your In Circuit Tester Performance
-

Understanding the Importance of Semiconductor Testing in Modern Technology
-

Top Trends in Semiconductor Test Sockets for 2025 You Need to Know
-

Exploring Market Trends for Air Presses at the 138th China Export and Import Fair 2025
